A few days ago I was greeted by this message when trying to access my k3s cluster:
1
|
Unable to connect to the server: x509: certificate has expired or is not yet valid
|
It meant that my k3s cluster is now officially one year old 🥳, but also meant that I needed to manually rotate the API server certificate.
As stated in a GitHub discussion: Understand k3s certificate rotation,
You don’t need to manually rotate them. As the docs say, the certs are renewed on startup if they are within 90 days of expiring.
the only thing I needed to do was to restart the k3s service on each master node.
But a great mind once said,
“Why spend 15 minutes to do a simple task when you can spend 4 hours automating it.”
so it was time for some automation.
Environment
- Kubernetes: v1.33.4+k3s1
- Master node VM OS: Debian 12 (x3)
- Hypervisor: Proxmox VE 8.4.14
Overview
As the official docs say:
K3s client and server certificates are valid for 365 days from their date of issuance.
and keys are automatically rotated when they are within 90 days of expiring, I just needed to make sure that k3s services are restarted regularly enough to catch the rotation window.
Theoretically, I could just restart the services once per year. If timing is set correctly, it should work.
Howerver I decided to be more proactive and restart the services every week. It would wouldn’t help, and may help catch any potential issues earlier.
Renewing server certs with Ansible
A simple Ansible playbook with k8s cronjob was all I needed.
hosts-configmap.yml
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: k3s-vms
namespace: ansible
data:
hosts.ini: |
[masters]
master_ip_1
master_ip_2
master_ip_3
[workers]
worker_ip_1
worker_ip_2
worker_ip_3
worker_ip_4
worker_ip_5
|
playbook-configmap.yml
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: restart-k3s-master
namespace: ansible
data:
restart.yml: |
- name: Restart k3s master nodes
hosts: masters
gather_facts: yes
vars:
ansible_ssh_common_args: "-o StrictHostKeyChecking=no"
tasks:
- name: Restart k3s service
systemd:
name: "{{ item }}"
state: restarted
loop:
- k3s
|
cronjob.yml
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
|
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: CronJob
metadata:
name: restart-k3s-master
namespace: ansible
spec:
timeZone: 'America/Denver'
schedule: "0 2 * * 6" # every Saturday at 2:00 AM
jobTemplate:
spec:
backoffLimit: 1
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: restart
image: alpine/ansible
command: ["ansible-playbook", "-i", "/etc/ansible-k3s/hosts.ini", "/etc/ansible-k3s/restart.yml"]
volumeMounts:
- name: hosts-config
mountPath: /etc/ansible-k3s/hosts.ini
subPath: hosts.ini
- name: restart-playbook
mountPath: /etc/ansible-k3s/restart.yml
subPath: restart.yml
- name: ssh-key
mountPath: /root/.ssh
readOnly: true
restartPolicy: Never
volumes:
- name: hosts-config
configMap:
name: k3s-vms
- name: restart-playbook
configMap:
name: restart-k3s-master
- name: ssh-key
secret:
secretName: pmx-vm-ssh
items:
- key: id_ed25519
path: id_ed25519
defaultMode: 0o600
|
secret.yml
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: pmx-vm-ssh
namespace: ansible
stringData:
id_ed25519: |
-----BEGIN OPENSSH PRIVATE KEY-----
[redacted]
-----END OPENSSH PRIVATE KEY-----
id_ed25519.pub: |
[redacted]
|
Now every k3s master node will have its k3s service restarted every Saturday at 2:00 AM.
Renewing client certs with GitLab CI
The official docs mentions:
K3s client and server certificates are valid for 365 days from their date of issuance.
Since client certificates also expire after one year, I wanted to automatically update them as well.
Luckily, my kubeconfig is managed in my GitLab repository, and auto updating a file on GitLab is a well-established process.
1
|
lrwxrwxrwx 1 jy jy 34 Oct 11 23:04 .kube/config -> /home/jy/git/homelab/kube/kube.yml
|
In the homelab repo, I created a GitLab CI job to obtain the new kubeconfig from one of the master nodes, and commit it back to the repo.
.gitlab-ci.yml
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
|
stages:
- update
update-kubeconfig:
stage: update
image: alpine:latest
rules:
- if: '$CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE == "schedule" && $CI_COMMIT_BRANCH == "master"'
before_script:
- apk add --no-cache openssh-client git yq
- mkdir -p ~/.ssh
- chmod 700 ~/.ssh
- cp ansible/vm/key/id_master_ed25519 ~/.ssh/id_master_ed25519
- chmod 600 ~/.ssh/id_master_ed25519
# Configure git
- git config --global user.email "ci@gitlab.com"
- git config --global user.name "GitLab CI"
- git remote set-url origin "https://oauth2:${GITLAB_PUSH_TOKEN}@${CI_SERVER_HOST}/${CI_PROJECT_PATH}.git"
- git checkout "${CI_COMMIT_BRANCH}"
- git pull origin "${CI_COMMIT_BRANCH}"
script:
# Get the original server URL from current kubeconfig
- ORIGINAL_SERVER=$(yq eval '.clusters[0].cluster.server' kube/kube.yml)
- echo "Original server URL is $ORIGINAL_SERVER"
# Fetch kubeconfig from HAProxy endpoint
- |
ssh -i ~/.ssh/id_master_ed25519 -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no root@10.0.69.239 \
"cat /etc/rancher/k3s/k3s.yaml" > kube/kube.yml.new
# Replace the server URL with the original (HAProxy endpoint)
- yq eval ".clusters[0].cluster.server = \"${ORIGINAL_SERVER}\"" -i kube/kube.yml.new
# Replace old kubeconfig
- mv kube/kube.yml.new kube/kube.yml
# Check for changes and commit if needed
- |
if git diff --quiet kube/kube.yml; then
echo "No changes detected in kubeconfig"
exit 0
else
echo "Changes detected, committing..."
git add kube/kube.yml
git commit -m "chore: update kubeconfig [skip ci]"
git push origin "${CI_COMMIT_BRANCH}"
fi
after_script:
- rm -f ~/.ssh/id_master_ed25519
|
When executed, it will
- SSH into one of the master nodes (via HAProxy)
- Grab the latest
/etc/rancher/k3s/k3s.yaml
- Update the server URL to point to the HAProxy endpoint
- Commit and push the updated kubeconfig back to the GitLab repo
Then I set it up to run every Saturday at 3:00 AM (one hour after the Ansible cronjob) using GitLab’s scheduled pipelines feature.
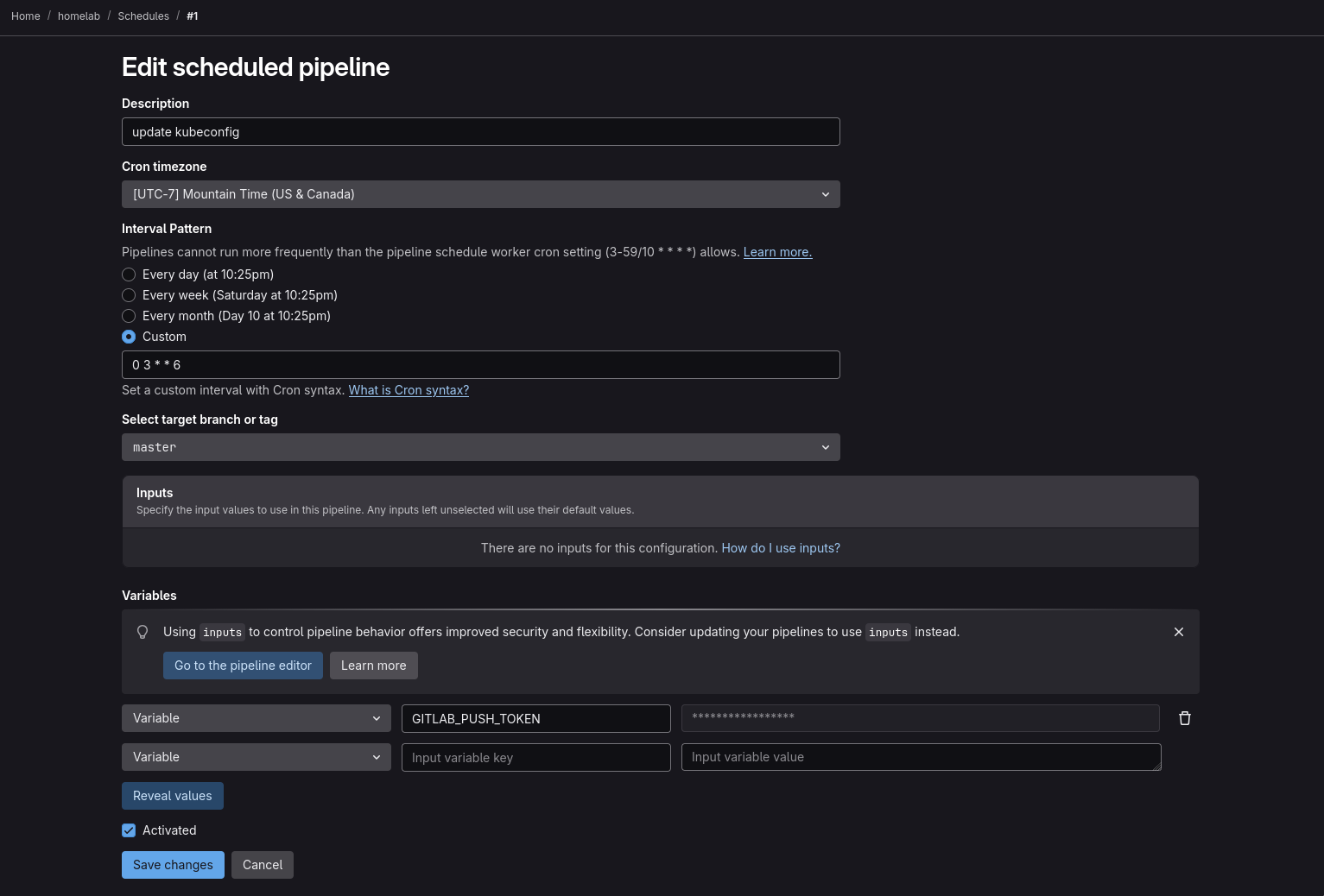
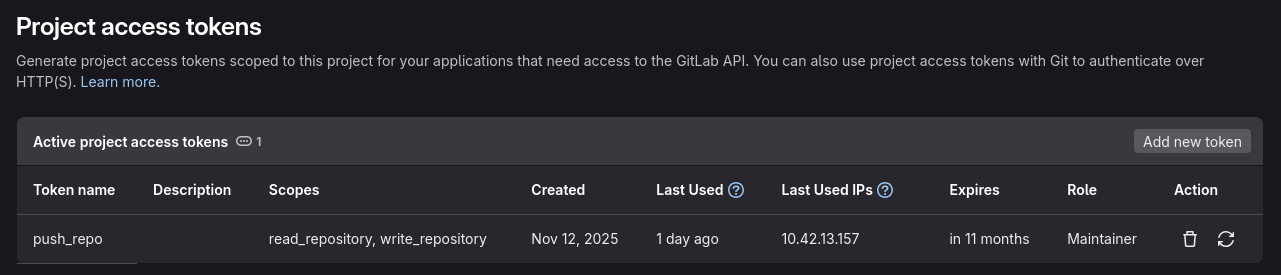
The GITLAB_PUSH_TOKEN variable is a project access token with scopes read_repository, write_repository.
Conclusion
From now on, each year, my k3s cluster’s server certificates will be automatically rotated at some point near expiration, and client certificates will be updated right after.
This setup has two issues that I can currently think of:
- If for some reason GitLab CI job fails but Ansible cronjob has succeeded, the kubeconfig in the repo will be out of date.
- Ansible job runs at 2AM and GitLab job at 3AM. If I’m working on something at that time, I would suddenly lose access to my cluster.
But until I find a better solution, this should work just fine.